|
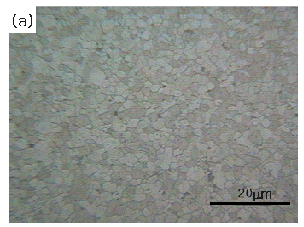 
Fig.
(a) shows microstructure of ZnO sintered
by UNICERA's Microwave Furnace at 1200¡É
for 5 minutes with heating rate of 100¡É/min.
Compared to Fig. (b) which shows microstructure
of ZnO sintered by a conventional electric
furnace at 1200¡É for 4 hours with heating
rate of 5¡É/min, Fig. (a) displays dense
microstructure with few pores in spite of
short sintering time. We can expect that, because
of the high heating rate and short sustaining
time, grain growth is almost prohibited.
In
addition, we can compare Zirconia sample
sintered by UNICERA's microwave furnace
with the one sintered by conventional Electric
furnace.
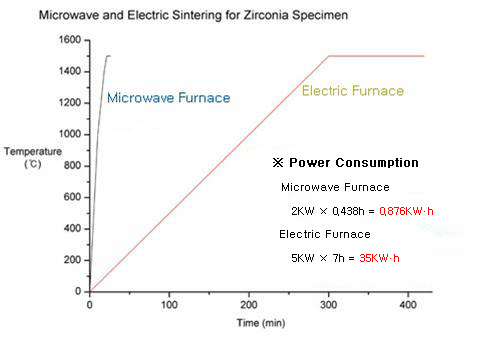
Fig.
(c)
Fig.
(c) shows the heating rate and duration
time of sintering by a Microwave furnace
and an Electric Furnace. As you can see,
by using a Microwave furnace, we raise the
temperature with the heating rate of 100¡É/min
up to 1000¡É and, with 50¡É up to 1400¡É
and then with 30¡É up to 1500¡É. We sustain
the temperature at 1500¡É for five minutes.
In contrast, by using an Electric furnace,
we raise the temperature with the heating
rate of 5¡É/min up to 1500¡É for 5 hours
and sustain the temperature at 1500¡É for
2 hours. The result of sintering following
these procedures are shown in pictures below:
.jpg)
.jpg)
Fig.
(d) Fig.
(e)
Fig.
(d) shows the microstructure of Zirconia
sintered bt an Elctric furnace and Fig.
(e) shows the microstructure of Zirconia
sintered by a Microwave furnace.
The
significant advantages of Microwave Sintering
include: (1) a short processing time
(shorter
than 1/20), (2) little
energy consumption (less
that 1/3), (3) increased
mechanical strength of a sintered material
owing to a high density and fine grain size.
|
